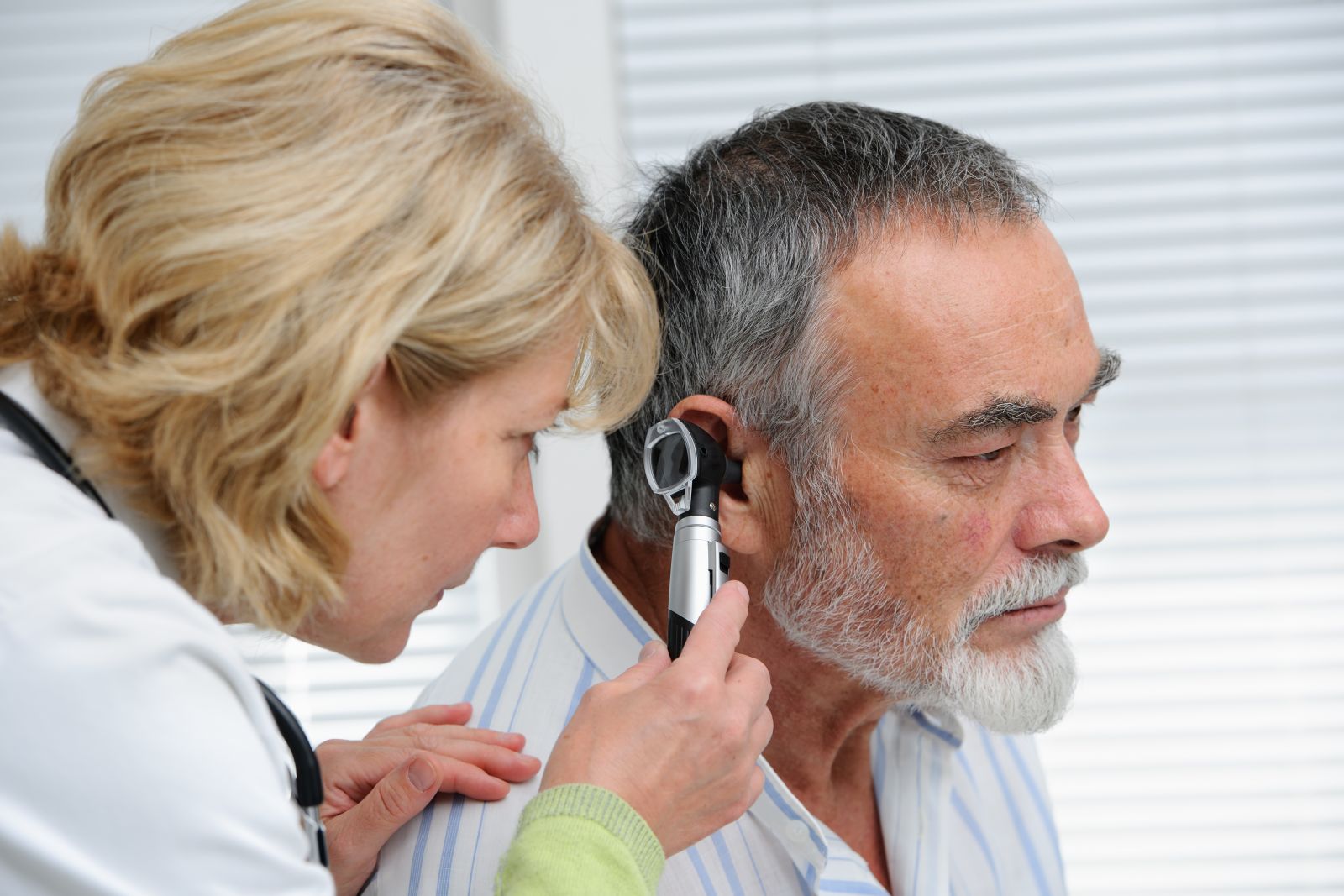
Understanding the difference between temporary and permanent hearing loss is crucial for managing your hearing health.
Here’s a breakdown of each and what you need to know:
Temporary Hearing Loss
Causes:
- Ear Infections: Middle ear infections or fluid build-up can cause temporary hearing loss.
- Exposure to Loud Noise: Brief exposure to very loud sounds (e.g., concerts or fireworks) can cause temporary hearing loss.
- Earwax Buildup: Excessive earwax can block the ear canal, leading to temporary hearing difficulties.
- Barotrauma: Changes in pressure (such as during air travel or scuba diving) can cause temporary hearing loss.
Symptoms:
- Muffled hearing or a sensation of fullness in the ear.
- Temporary decrease in hearing ability.
- Usually accompanied by other symptoms of the underlying cause (e.g., pain from an infection).
Diagnosis:
- A physician can diagnose temporary hearing loss and decide on the appropriate next steps for treatment. That could mean treatments such as (but not limited to) ear wax removal, antibiotics, a hearing test or a referral to an ENT specialist.
- Medical history and examination of the ear may also provide clues.
Treatment:
- Often resolves on its own once the underlying cause is treated (e.g., antibiotics for infections, earwax removal).
- Avoiding further exposure to loud noises and using ear protection can prevent recurrence.
Permanent Hearing Loss
Causes:
- Age-Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis): Gradual loss of hearing due to aging.
- Genetic Factors: Inherited conditions that affect hearing.
- Prolonged Exposure to Loud Noise: Chronic exposure to loud environments can cause permanent damage.
- Ototoxic Medications: Certain medications can damage the inner ear structures.
- Trauma or Injury: Physical injury to the ear or head can cause permanent hearing loss.
Symptoms:
- Persistent difficulty hearing even in quiet environments.
- Trouble understanding speech, especially in noisy settings.
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus) that doesn’t go away.
Diagnosis:
- Comprehensive hearing tests.
- Additional imaging or evaluations by an ENT specialist might be needed to determine the extent and cause. This is often determined by the results of the initial hearing test and a physician.
Treatment:
- Hearing Aids: Can amplify sounds and improve hearing ability by enhancing speech clarity.
- Cochlear Implants: For those with severe to profound hearing loss, these devices can provide a sense of sound.
- Assistive Listening Devices: Include different technologies that help with communication. These devices can be portable microphones and TV streamers. They improve how hearing aids work.
- Rehabilitation: Speech therapy and auditory training can help adapt to hearing loss. It is important to have family, friends and caregivers involved whenever possible as communication is a two-way street.
Key Points to Remember
- Seek Professional Advice: If you experience sudden or severe hearing loss, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can sometimes prevent further damage or help manage the condition more effectively.
- Monitor Changes: Keep track of any changes in your hearing and inform your healthcare provider. Even if your hearing loss is temporary, it’s important to understand the cause and prevent recurrence.
- Protect Your Hearing: Avoid exposure to loud noises and use hearing protection if you’re in a noisy environment. This can help prevent both temporary and permanent hearing loss.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups with a hearing healthcare professional can help manage and monitor your hearing health, especially if you have a history of hearing issues.
If you have specific concerns or symptoms, contact us at Academy Hearing Centres. We will assess your situation and either book a hearing test or direct you to the most appropriate healthcare provider for your needs.